“Farming in the Dark of the Market: Unraveling the Mysteries of Cryptos, Whales, and Gas Prices”
The world of cryptocurrency has become increasingly complex, with many players vying for attention and profits. One of the key factors driving price movements is the order book, a critical component of the market that determines how much liquidity is available to traders.
Order Book: The Backbone of Cryptocurrency Trading
An order book is essentially a list of buy and sell orders that are waiting to be executed by market makers or other traders. It’s like a virtual auction house where buyers and sellers can place their bids and offers at any given time. When two parties agree on a price, the order is filled, and the transaction occurs.
In a traditional exchange like Bitcoin, the order book would display buy and sell orders side by side, showing the current prices of different coins. However, with decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like Binance or Kraken, the order book has evolved to resemble a giant list of pending trades. This allows traders to view all available orders at any given time, making it easier to identify profitable opportunities.
Whales: The Titans of Cryptocurrency Trading
Cryptocurrencies have attracted some of the most powerful players in finance, known as “whales.” These individuals have an enormous amount of capital and influence that can significantly impact market prices. Whales often hold large amounts of coins, which they can use to manipulate the market or trade with other prominent traders.
Some notable whales include Vitalik Buterin (ETH), the creator of Ethereum, and Satoshi Nakamoto (BTC), the anonymous founder of Bitcoin. These individuals have enormous influence over the market, and their trades can drive prices up or down by hundreds or even thousands of dollars per coin.
Gas: The Hidden Cost of Cryptocurrency Transactions
When it comes to buying and selling cryptocurrencies, one often-overlooked expense is gas (gas fee). Gas refers to the cost of executing transactions on a blockchain network. This includes the fees paid to miners who validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the network.
The amount of gas required for a transaction can vary greatly depending on factors such as network congestion, block size, and network activity. To give you an idea of just how expensive it is to do business in cryptocurrency, imagine paying $100,000 or more to execute just one transaction!
Conclusion
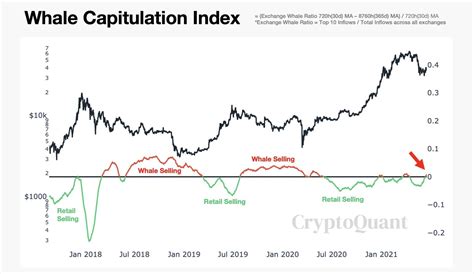
In conclusion, the world of cryptocurrency trading is full of complex mechanics that can be difficult to understand. The order book provides a critical layer of liquidity and transparency, while whales wield enormous influence over market prices. Gas fees are another hidden expense that can significantly impact transactions. By grasping these fundamentals, traders and investors can make more informed decisions and navigate the wild world of cryptocurrency trading with confidence.
I hope you found this article informative!
